
For instance, floods are more frequent in rural western parts of Kenya. Preliminary results show significant variability in both risks and needs within and between countries. Household surveys and focus group discussions were conducted in 36 communities in Kenya, Ghana and Burkina Faso in order to identify relevant climate related hazards, current response strategies and early warning needs. The project seeks to identify how governments can better communicate risks by designing multi-hazard early warning systems that deliver actionable warnings across timescales. This presentation will review research results of the United Nations Environment Programme's CLIM- WARN project. Although great strides have been made in developing early warning systems most deal with one hazard, only provide short-term warnings and do not reach the most vulnerable. Habilov, M.Įarly warning systems are a tool with which to minimize risks posed by climate related hazards. Managing Risks? Early Warning Systems for Climate Change
Coolterm 104 framing error portable#
Because the prototype system demonstrated that potentially useful warnings of strong shaking from aftershocks are feasible, the USGS has completed a portable early warning system for aftershocks that can be deployed anywhere. In its first 6 months of operation, the system generated triggers for all 12 M > 3.7 aftershocks for which trigger documentation is preserved, did not trigger on any M ≦ 3.6 aftershocks, and produced one false trigger as a result of a now-corrected single point of failure design flaw.

One of the radio receivers was deployed at the California Department of Transportation (CALTRANS) headquarters at the damaged Cypress Street section of the I-880 freeway in Oakland, California on 28 October 1989 and provided about 20 sec of warning before shaking from the M 4.5 Loma Prieta aftershock that occurred on 2 November 1989 at 0550 UTC.
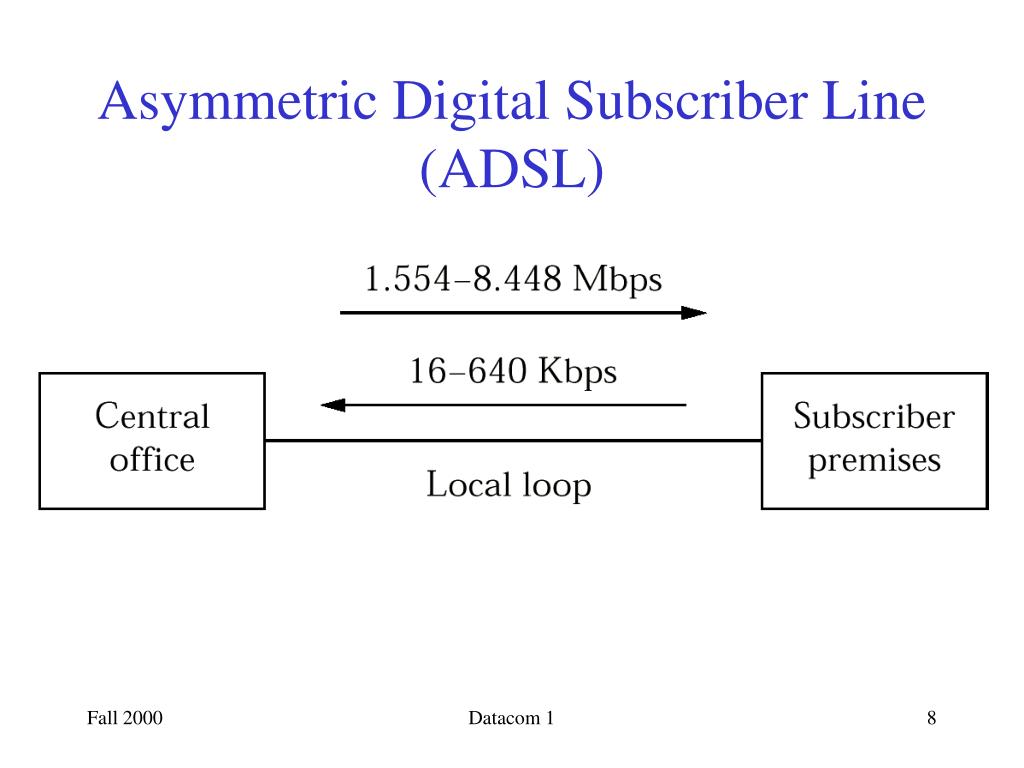
The prototype system consisted of four components: ground motion sensors in the epicentral area, a central receiver, a radio repeater, and radio receivers. VanSchaack, J.Ī prototype early warning system to provide San Francisco and Oakland, California a few tens-of-seconds warning of incoming strong ground shaking from already-occurred M ≧ 3.7 aftershocks of the magnitude 7.1 17 October 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake was operational on 28 October 1989. To effectively reduce maternal, risk early warning systems that capture deterioration from a broad range of conditions may be required in addition to bundles tailored to specific conditions such as hemorrhage, thromboembolism, and hypertension.īakun, W.H. Evolving data on outcomes on early warning systems suggest that maternal risk may be reduced.

Successful implementation of early warnings systems requires administrative and leadership support, dedication of resources, improved coordination between nurses, providers, and ancillary staff, optimization of information technology, effective education, evaluation of and change in hospital culture and practices, and support in provider decision-making. While implementation experiences varied based on factors specific to individual sites, common themes relevant to all hospitals presenting were identified. This manuscript reports on key points from this session. Given current interest in early warning systems and their potential role in care, the 2017 Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM) Annual Meeting dedicated a session to exploring early warning implementation across a wide range of hospital settings. While literature on outcomes and test characteristics of maternal early warning systems is evolving, there is limited guidance on implementation. Severe maternal morbidity and mortality are often preventable and obstetric early warning systems that alert care providers of potential impending critical illness may improve maternal safety.

Implementing Obstetric Early Warning Systems.įriedman, Alexander M Campbell, Mary L Kline, Carolyn R Wiesner, Suzanne D'Alton, Mary E Shields, Laurence E


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
